Esch, T. & Stefano, G. B. The neurobiology of pleasure, reward processes, addiction and their health implications. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 25(4), 235–251 (2004).
Speranza, L., di Porzio, U., Viggiano, D., de Donato, A. & Volpicelli, F. Dopamine: The neuromodulator of long-term synaptic plasticity, reward and movement control. Cells 10(4), 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040735 (2021).
Jenkins, G. & Walton, M. Dopamine: Don’t underestimate the force. Curr. Biol. 30(14), R824–R826 (2020).
Lambrini, K. et al. Sleep and health: Role of dopamine.In Proc Dopamine, Health Disease. 31 (2018).
Lee, J. Y. et al. Dopamine facilitates associative memory encoding in the entorhinal cortex. Nature 598(7880), 321–326 (2021).
Mohebi, A. et al. Dissociable dopamine dynamics for learning and motivation. Nature 570(7759), 65–70 (2019).
Cheng, Y. T. et al. Social deprivation induces astrocytic TRPA1-GABA suppression of hippocampal circuits. Neuron 111(8), 1301–1315 (2023).
Prevot, T. & Sibille, E. Altered GABA-mediated information processing and cognitive dysfunctions in depression and other brain disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 26(1), 151–167 (2021).
Tinok, A. A., Karabay, A., Jong, J., Balta, G. & Akyurek, E. G. Effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid on working memory and attention: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. J. Psychopharmacol. 37(6), 554–565 (2023).
Martel, J. C. & Gatti, M. S. Dopamine receptor subtypes, physiology and pharmacology: New ligands and concepts in schizophrenia. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 1003 (2020).
Lee, B. E. et al. O-GlcNAcylation regulates dopamine neuron function, survival and degeneration in Parkinson disease. Brain 143(12), 3699–3716 (2020).
Pristera, A. et al. Dopamine neuron-derived IGF-1 controls dopamine neuron firing, skill learning, and exploration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. u. s. a 116(9), 3817–3826 (2019).
Cheng, Z. Y., Hu, Y. H., Xia, Q. P., Wang, C. & He, L. DRD1 agonist A-68930 improves mitochondrial dysfunction and cognitive deficits in a streptozotocin-induced mouse model. Brain Res. Bull. 175, 136–149 (2021).
Cheng, Z. Y., Xia, Q. P., Hu, Y. H., Wang, C. & He, L. Dopamine D1 receptor agonist A-68930 ameliorates Abeta(1–42)-induced cognitive impairment and neuroinflammation in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 88, 106963 (2020).
Moritz, A. E. et al. Discovery, optimization, and characterization of ML417: A novel and highly selective D(3) dopamine receptor agonist. J. Med. Chem. 63(10), 5526–5567 (2020).
Nair-Roberts, R. G. et al. Stereological estimates of dopaminergic, GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area, substantia nigra and retrorubral field in the rat. Neuroscience 152(4), 1024–1031 (2008).
Zhou, F. W., Jin, Y., Matta, S. G., Xu, M. & Zhou, F. M. An ultra-short dopamine pathway regulates basal ganglia output. J. Neurosci. 29(33), 10424–10435 (2009).
Boyson, S. J., McGonigle, P. & Molinoff, P. B. Quantitative autoradiographic localization of the D1 and D2 subtypes of dopamine receptors in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 6(11), 3177–3188 (1986).
Savasta, M., Dubois, A. & Scatton, B. Autoradiographic localization of D1 dopamine receptors in the rat brain with [3H]SCH 23390. Brain Res. 375(2), 291–301 (1986).
Wamsley, J. K., Gehlert, D. R., Filloux, F. M. & Dawson, T. M. Comparison of the distribution of D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors in the rat brain. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2(3), 119–137 (1989).
Dawson, T. M., Barone, P., Sidhu, A., Wamsley, J. K. & Chase, T. N. The D1 dopamine receptor in the rat brain: Quantitative autoradiographic localization using an iodinated ligand. Neuroscience 26(1), 83–100 (1988).
Trevitt, T. et al. Interactions between dopamine D1 receptors and gamma-aminobutyric acid mechanisms in substantia nigra pars reticulata of the rat: Neurochemical and behavioral studies. Psychopharmacology 159(3), 229–237 (2002).
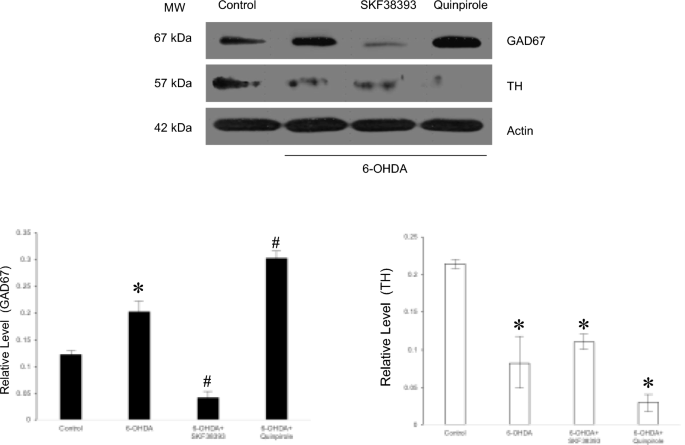
Yamamoto, N. & Soghomonian, J. J. Time-course of SKF-81297-induced increase in glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 and 67 mRNA levels in striatonigral neurons and decrease in GABA(A) receptor alpha1 subunit mRNA levels in the substantia nigra, pars reticulata, in adult rats with a unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesion. Neuroscience 154(3), 1088–1099 (2008).
Pan, H. S., Penney, J. B. & Young, A. B. Gamma-aminobutyric acid and benzodiazepine receptor changes induced by unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the medial forebrain bundle. J. Neurochem. 45(5), 1396–1404 (1985).
Jayatilleke, K. M. & Hulett, M. D. Heparanase and the hallmarks of cancer. J. Transl. Med. 18(1), 453 (2020).
Brewer, G. J. & Torricelli, J. R. Isolation and culture of adult neurons and neurospheres. Nat. Protoc. 2(6), 1490–1498 (2007).
Paxinos G, Franklin KB. Paxinos and Franklin’s the Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates(Academic Press, 2019).
Radnikow, G. & Misgeld, U. Dopamine D1 receptors facilitate GABAA synaptic currents in the rat substantia nigra pars reticulata. J. Neurosci. 18(6), 2009–2016 (1998).
Oertel, W. H., Tappaz, M. L., Berod, A. & Mugnaini, E. Two-color immunohistochemistry for dopamine and GABA neurons in rat substantia nigra and zona incerta. Brain Res. Bull. 9(1–6), 463–474 (1982).
Yadav, R. K., Khanday, M. A. & Mallick, B. N. Interplay of dopamine and GABA in substantia nigra for the regulation of rapid eye movement sleep in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 376, 112169 (2019).
Maingret, F. & Groc, L. Characterization of the functional cross-talk between surface GABA(A) and dopamine D5 receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22(9), 4867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094867 (2021).
Villalobos-Escobedo, F. S. et al. Dopamine D3 receptor modulates D2 receptor effects on cAMP and GABA release at striatopallidal terminals-Modulation by the Ca2+-Calmodulin-CaMKII system. Eur. J. Neurosci. 59(7), 1441–1459. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.16237(2023).
Negrete-Diaz, J. V. et al. Pharmacological activation of dopamine D(4) receptor modulates morphine-induced changes in the expression of GAD(65/67) and GABA(B) receptors in the basal ganglia. Neuropharmacology 152, 22–29 (2019).
Tan, T. et al. Stress exposure in dopamine D4 receptor knockout mice induces schizophrenia-like behaviors via disruption of GABAergic transmission. Schizophr. Bull. 45(5), 1012–1023 (2019).
Erlander, M. G. & Tobin, A. J. The structural and functional heterogeneity of glutamic acid decarboxylase: A review. Neurochem. Res. 16(3), 215–226 (1991).
Pinal, C. S. & Tobin, A. J. Uniqueness and redundancy in GABA production. Perspect. Dev. Neurobiol. 5(2–3), 109–118 (1998).
Chattopadhyaya, B. et al. GAD67-mediated GABA synthesis and signaling regulate inhibitory synaptic innervation in the visual cortex. Neuron 54(6), 889–903 (2007).
Zhang, K., Chammas, C. & Soghomonian, J. J. Loss of glutamic acid decarboxylase (Gad67) in striatal neurons expressing the Drdr1a dopamine receptor prevents L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned mice. Neuroscience 303, 586–594 (2015).
Li, X. et al. Exercise training modulates glutamic acid decarboxylase-65/67 expression through TrkB signaling to ameliorate neuropathic pain in rats with spinal cord injury. Mol. Pain. 16, 1744806920924511 (2020).
Jaber, M., Robinson, S. W., Missale, C. & Caron, M. G. Dopamine receptors and brain function. Neuropharmacology 35(11), 1503–1519 (1996).
Vasudevan, A. et al. Dopaminergic neurons modulate GABA neuron migration in the embryonic midbrain. Development 139(17), 3136–3141 (2012).
Soghomonian, J. J., Gonzales, C. & Chesselet, M. F. Messenger RNAs encoding glutamate-decarboxylases are differentially affected by nigrostriatal lesions in subpopulations of striatal neurons. Brain Res. 576(1), 68–79 (1992).
Laprade, N. & Soghomonian, J. J. Glutamate decarboxylase (GAD65) gene expression is increased by dopamine receptor agonists in a subpopulation of rat striatal neurons. Mol. Brain Res. 48(2), 333–345 (1997).
Lee, M., Schwab, C. & McGeer, P. L. Astrocytes are GABAergic cells that modulate microglial activity. Glia 59(1), 152–165 (2011).
Zhang, X. et al. NG2 glia-derived GABA release tunes inhibitory synapses and contributes to stress-induced anxiety. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 5740 (2021).
Zhang, Y. et al. Mapping heparanase expression in the spinal cord of adult rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 494(2), 345–357 (2006).
Bishop, J. R., Schuksz, M. & Esko, J. D. Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature 446(7139), 1030–1037 (2007).
Qiu, H., Yang, B., Pei, Z. C., Zhang, Z. & Ding, K. WSS25 inhibits growth of xenografted hepatocellular cancer cells in nude mice by disrupting angiogenesis via blocking bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)/Smad/Id1 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 285(42), 32638–32646 (2010).
Yamaguchi, Y. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans in the nervous system: Their diverse roles in neurogenesis, axon guidance, and synaptogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 12(2), 99–106 (2001).
Kaksonen, M. et al. Syndecan-3-deficient mice exhibit enhanced LTP and impaired hippocampus-dependent memory. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 21(1), 158–172 (2002).
Nyhus, J. K. & Denburg, J. L. The in vivo regulation of pioneer axon growth by FGF-2 and heparan sulfate proteoglycans in cultured embryos of the cockroach. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 11(5–6), 305–323 (1998).
Walz, A. et al. Essential role of heparan sulfates in axon navigation and targeting in the developing visual system. Development 124(12), 2421–2430 (1997).
Xiong, A., Spyrou, A. & Forsberg-Nilsson, K. Involvement of heparan sulfate and heparanase in neural development and pathogenesis of brain tumors. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1221, 365–403 (2020).






Leave feedback about this