:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(jpeg)/VWH-GettyImages-1162661505-7159c6fde0b047219d00c29883e87e7f.jpg)
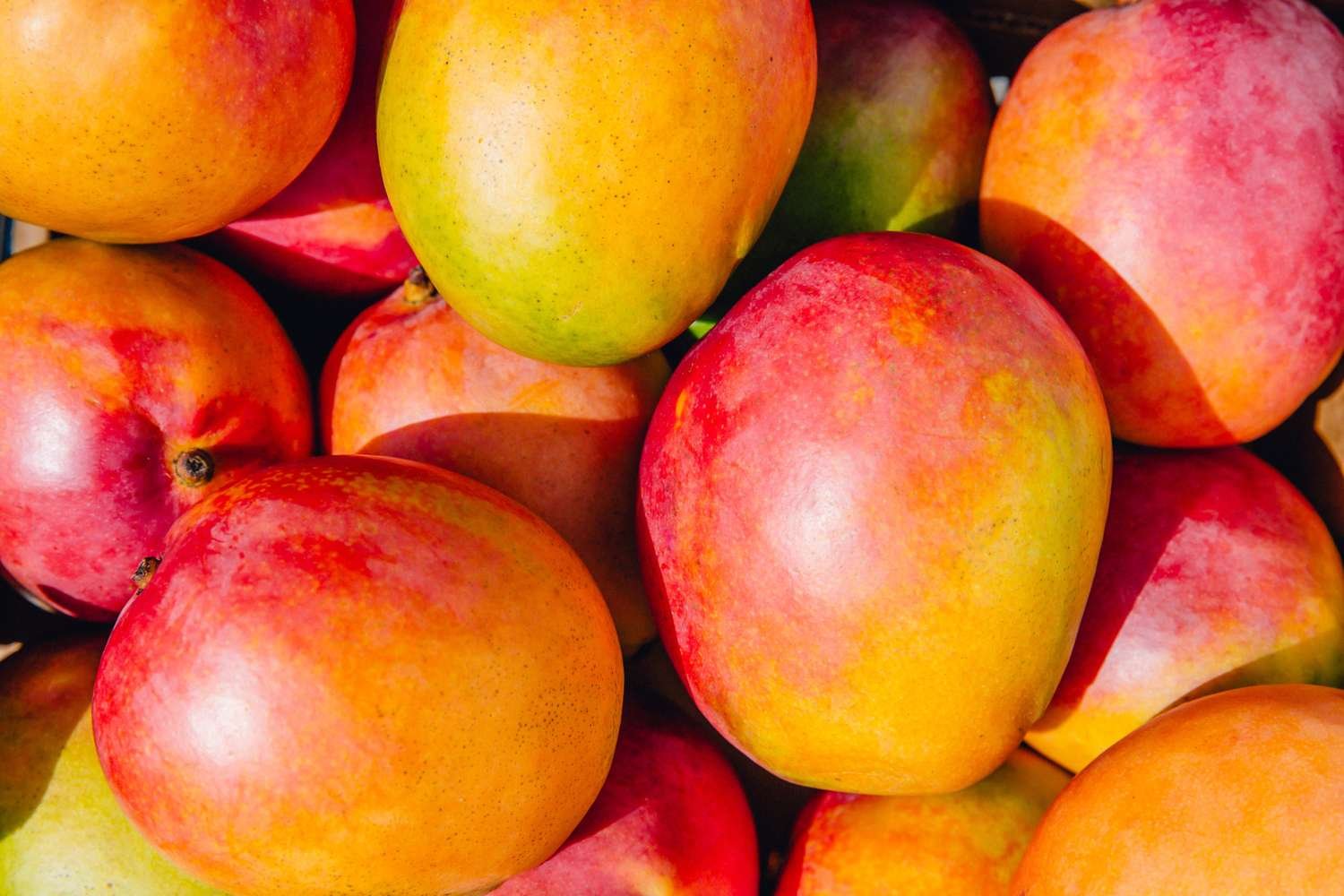
Mangoes are a sweet, tropical, nutritious fruit that offers multiple potential health benefits, such as protecting against heart disease and improving eye and skin health.
Jump to Key Takeaways.
1. Boosts Nutrient Intake
In addition to being low-calorie, mangoes are a rich source of essential nutrients that support the immune system, digestion, and more. These include:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin C
- Fiber
- Vitamin B6
- Folate
- Magnesium
- Potassium
2. Supports Immune Health
Mangoes support the immune system thanks to their rich content of vitamins and antioxidants. Specifically, the amount of vitamin C in mangoes helps strengthen the body’s defenses against illness and infection, while the antioxidant carotenoid beta carotene can help boost overall immunity.
3. Improves Digestion
The fiber content of mangoes makes this fruit helpful for digestive health, allowing for regular bowel movements. One study showed that people who ate one or two mangoes daily over four weeks experienced improvements in digestive-related issues like constipation.
4. Fights Inflammation
The antioxidants and other nutrients found in mangoes contain anti-inflammatory properties. Research shows that antioxidants like quercetin and mangiferin can help fight the development of chronic disease by reducing inflammation.
5. Protects Eye Health
Beta carotene is key for improving eye health and is plentiful in mangoes. Other carotenoids that mangoes contain, like lutein and zeaxanthin, protect the eye’s retina and lens by reducing discomfort from lighting and glare and enhancing visual contrast and range.
6. Helps With Weight Management
While mangoes may be known for their sweet flavor, they can still be helpful for weight management. Though it’s a source of natural sugar, this fruit is low in calories and high in fiber, which helps promote the feeling of fullness and prevents constipation, supporting weight loss goals.
7. Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
Consuming mangoes daily may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity and maintaining blood sugar levels in people with obesity or excess weight. Mangoes contain fiber to help regulate blood sugar levels, and they rank low to moderate on the glycemic index (GI), meaning it doesn’t lead to rapid blood sugar spikes.
8. Reduces Heart Disease Risk
Eating mangoes might protect the heart by managing blood cholesterol levels. Mangiferin, an antioxidant found in mangoes, is linked to decreased blood lipid levels and inflammation, which can reduce the risk of developing heart disease.
9. Prevents Cancer
Polyphenols (antioxidants) are plentiful in mangoes and can be found in the fruit’s pulp, peel, and seeds. Research shows that consuming mangoes regularly promotes antioxidant activity that protects the body’s cells from damage, which can help prevent the development of chronic diseases like cancer and type 2 diabetes.
10. Strengthens Bones, Skin, and Hair
Because mangoes contain copious amounts of vitamins A, C, and E and calcium, it’s a key fruit for boosting skin, hair, and bone health. Vitamin C is necessary for the body to produce collagen. This protein supports skin elasticity and anti-aging, while vitamins A and E are crucial for nourishing healthy skin and hair.
What’s more, mangoes’ rich calcium content can strengthen bone health and potentially protect against bone disease like osteoporosis.
11. Enhances Energy and Brain Function
The carbohydrates and fiber found in mangoes offer a combination that can help maintain energy and blood sugar levels throughout the day. Initial research also suggests that mango and mango leaf extract may boost cognitive function, improving mental tasks like memory, attention, response, and learning.
How to Incorporate Mangoes Into Your Diet
Mangoes are a perfect fruit to add to your breakfast, lunch, dinner, or snack. They can be eaten fresh, frozen, or dried, and used as a topping, side, smoothie ingredient, or dessert.
Depending on when you want to eat them, be sure to store mangoes properly for the best flavor and freshness. Some mangoes may last up to eight days at room temperature, while storing them in a refrigerator can increase their shelf life to three weeks.
Are There Any Risks?
Mangoes are generally safe to eat, except in a few circumstances. For example, they may lead to:
- Digestive symptoms: Because mangoes contain carbohydrates that are hard to digest, they can lead to digestive-related symptoms like gas and bloating in some people.
- Sugar overload: People following a low-sugar diet and people with diabetes may want to be mindful of mango portions due to the fruit’s high carbohydrate content.
- Allergic reactions: Though it’s rare, some people may experience an allergic reaction to mangoes. These reactions can happen when they come into physical contact with the skin or flesh of a mango or after consuming it.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
See a healthcare provider if you notice signs of a mango allergic reaction, such as:
- Itchiness, tingling, and swelling of the mouth, face, lips, and tongue
- Throat tightness or swelling
- Wheezing
- Hives
Key Takeaways
- Mangoes are a rich source of various vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Research suggests that consuming this versatile fruit regularly may offer potential health benefits, including supporting heart health, the immune system, digestion, and more.
- Keep in mind that eating mangoes may not be right for everyone, especially if you have a digestive disorder, diabetes, or experience an allergic reaction to the fruit. Consider checking with a healthcare provider before making any major dietary changes.













Leave feedback about this