Spending time outdoors during the summer months can help you stay active and healthy. While you’re out and about, it’s essential to protect your skin from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays.
Jump to Key Takeaways.
1. Use Sunscreen
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays:
Sunscreen should have a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 15. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends using a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
Sunscreen tips include:
- Apply sunscreen generously to dry skin 15 minutes before going outdoors. Use about 1 ounce (about as much as fills a shot glass) on any uncovered skin areas, including the neck, face, ears, hands, and feet..
- Reapply the sunscreen every two hours, or more often if you are swimming or sweating.
- Use only sunscreen formulations in lotions, creams, gels, sprays, and butter formulations. Avoid using sunscreen in other forms, including wipes, body wash, and shampoo.
2. Cover Exposed Skin
On extremely sunny days, it is a good idea to cover exposed skin. The clothes you wear will provide different levels of UV protection.
Sun protective clothing includes:
- Long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and long skirts
- Dark colors, which provide more protection than light colors
- Tightly woven fabrics that protect better than loose-woven clothing
- Dry fabrics over wet fabrics
Not all clothing offers UV protection. If light can get through fabric, so can UV rays.
If you spend a lot of time in the sun, consider clothing with a high UV protection factor. This sun-protective clothing is made from tightly woven fabrics with UV-blocking effects.
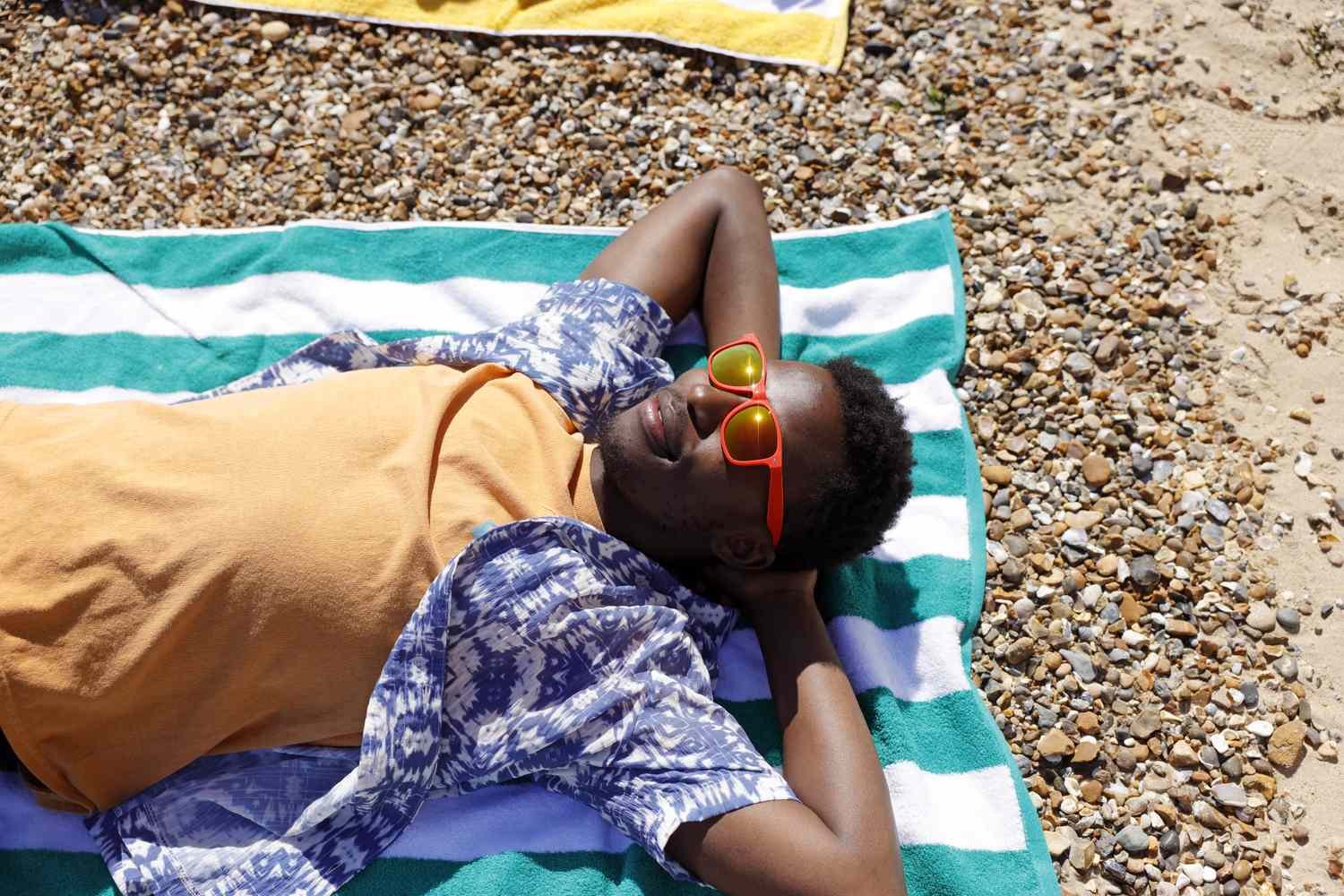
3. Wear Sunglasses
UV-blocking sunglasses can protect the eyes and the delicate skin around them. The ideal sunglasses should block at least 99% to 100% of UVA and UVB rays.
Sunglasses that offer 99% to 100% protection will have labels stating, “UV absorption up to 400 nm” or “meets ANSI UV requirements.”
If glasses are marked “cosmetic,” they only block about 70% of UV rays. If there is no label, you cannot confirm whether they block any UV radiation.
4. Wear a Wide-Brimmed hat
Select a hat with a wide brim measuring at least 2 to 3 inches around to ensure adequate sun protection. This will help shield areas of the head and face most vulnerable to strong sunlight, such as the ears, eyes, forehead, nose, and scalp.
5. Stay Indoors When the Sun is the Most Intense
The sun is the most intense during the hours of 10:00 a.m. and 4:00 p,m. The sun’s most dangerous rays, called UVB rays, are the strongest during these hours.
In the hottest part of the day, it is also a good idea to keep windows shut and blinds and curtains closed. Utilize air conditioning and fans to keep your home cool and comfortable.
6. Get Shade
If you are out in the sun and your shadow is shorter than you are, this is the time when the sun’s rays are the most intense and dangerous. If you are outdoors during these times, try to stay under trees or canopies, or use a portable sunshade.
7. Stay Hydrated
Sun exposure can lead to dehydration and dry, irritated skin that is more susceptible to damage. While individual needs vary, drink whenever you are thirsty and aim to drink at least eight glasses of water daily. Increase your fluid intake during hot, summer days and while spending time outdoors.
8. Check the UV Index
The National Weather Service and the Environmental Protection Agency issue the UV Index forecast. The UV index is a forecast of the expected risk of exposure to UV radiation from the sun.
A UV index of 7 or higher could mean a high risk from unprotected sun exposure. With these levels, extra skin and eye protection is needed. For highly susceptible people (older adults, young children, and people with severe health conditions), protection may mean staying indoors.
The highest UV levels are typically between 10:00 a.m. and 4:00 p.m.
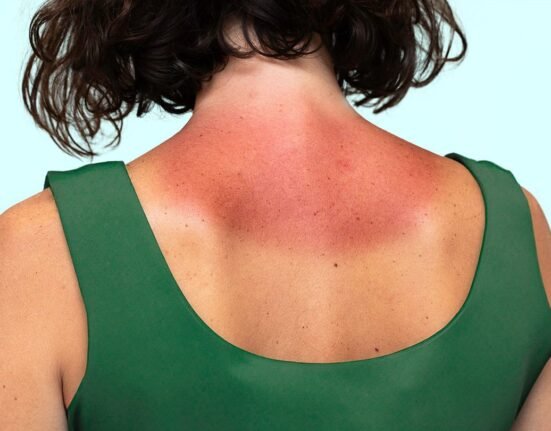
9. Practice After-Sun Care
Overexposure can still happen despite good skin care protection. After-sun care supports skin recovery and helps limit damage.
If you get sunburned, take action to:
- Cool your skin: Use cold compresses or a cool bath to reduce swelling and redness.
- Moisturize: Use aloe vera gel or other moisturizer ingredients to soothe the skin and keep it hydrated.
- Stay hydrated: Drink extra water to replenish and rehydrate your body.
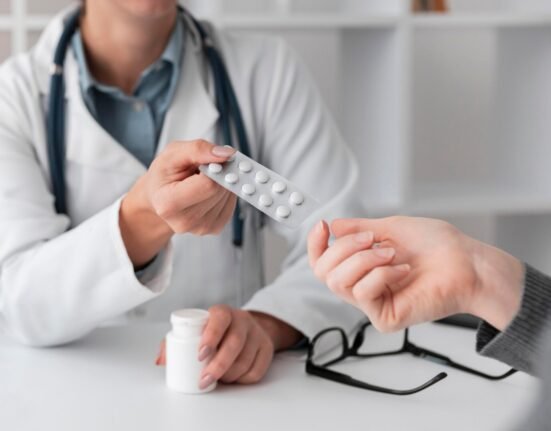
10. Be Mindful of Medications
Some medications may increase the risk of sun-induced skin damage. This includes antibiotics and medicines used to treat acne, mood disorders, high blood pressure, allergies, and autoimmune arthritis conditions.
Some over-the-counter skin care products that contain alpha- or beta-hydroxy acids or retinols may also make you more susceptible to damage from the sun.
If you are taking prescription medications and spend a lot of time outdoors, consult your healthcare provider to determine if you need to limit sun exposure or take extra precautions.
Key Takeaways
- Protecting the skin from the sun’s harmful effects is crucial when spending time outdoors during the summer months.
- Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15 to protect skin that is not covered by clothing; however, higher SPFs can offer additional protection.
- Additional ways to protect your skin include wearing clothing that covers the arms and legs, a wide-brimmed hat to protect the head, neck, and face, and sunglasses that block UV rays to protect your eyes and the surrounding skin.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/lana-barhum-d731df9d86514add9c6e1bd5aa2d7233.jpg)





Leave feedback about this